Alzheimer’s Stages
Intro
Welcome back to the professional blog. Alzheimer’s Stages. Intending to provide valuable insights into the stages and progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
Fully comprehending the passage from mild memory loss to severe cognitive decline is essential for effectively supporting loved ones.
By focusing on the different stages of Alzheimer’s, the individual’s challenges can be better understood, empowering individuals to receive the needed care and assistance.
Join this journey to understand the various stages of this disease, equipping individuals; the goal is to positively impact the lives of individuals impacted by Alzheimer’s disease.
Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease, a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, requires a comprehensive understanding of its stages to manage and support effectively.
With an expanding prevalence worldwide, it is crucial to comprehend the journey from mild memory loss to severe cognitive decline.
By familiarization with the phases, it is possible to assist loved ones in successfully navigating this challenging disease.
This article describes the various stages of Alzheimer’s, ranging from preclinical to severe, along with illustrating the characteristic symptoms and challenges faced.
Additionally, strategies for caretaking will be discussed, and the importance of gaining deeper insights into Alzheimer’s stages to improve the quality of life for those affected.
Definition and background of Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer’s is a gradually developing brain disorder that affects memory, thinking, and behavior. It accounts for approximately 60-80% of all dementia cases.
The disease was initially discovered by Dr. Alois Alzheimer in 1906. Alzheimer’s disease generally begins with moderate memory loss, but as it progresses, it causes severe cognitive decline that impedes daily activities.
Knowing the stages associated with Alzheimer’s is crucial to caregivers and family members as it assists in anticipating and planning for the needs of their loved ones.
Recognizing these stages may also aid healthcare professionals in providing appropriate care and support.
Importance of understanding the stages of Alzheimer’s disease
Understanding the stages associated with Alzheimer’s disease is vital to assist those living with the condition effectively.
Caregivers and healthcare professionals can tailor their approaches and interventions to each stage by elaborating on the disease progression.
Recognizing the steps, from mild to severe memory loss, enables better planning, management, and provision of appropriate resources.
Furthermore, comprehending the stages can alleviate the frustration and difficulties faced by those with Alzheimer’s and their loved ones, resulting in a higher quality of life and overall well-being.
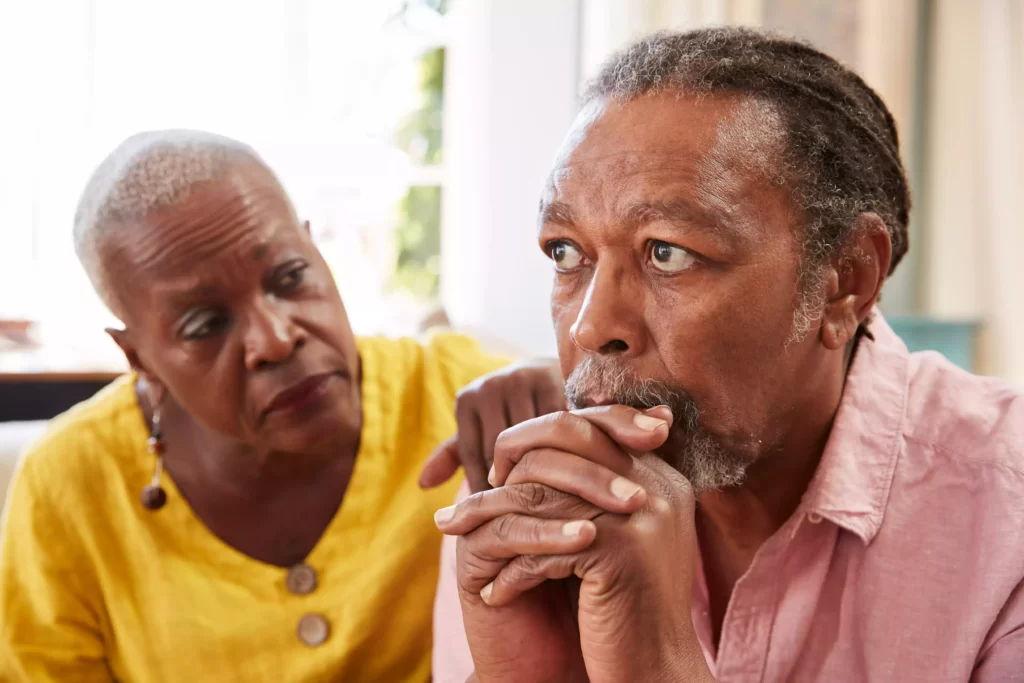

Stage 1: Preclinical Alzheimer’s
Stage 1: Preclinical Alzheimer’s is the initial phase of the disease, exhibited by the absence of noticeable symptoms.
During this phase, individuals may notice subtle changes in their brain function that are not yet apparent in their daily lives.
Diagnostic tests for early changes, such as brain imaging or cerebrospinal fluid analysis, are crucial to identifying these early changes.
Preclinical Alzheimer’s must be identified and diagnosed early to ensure that early intervention and future treatment can be implemented.
Research is underway to develop effective therapies that prevent or slow the progression of the disease in this phase.
Preclinical Alzheimer’s can provide the opportunity to strategize and prepare for the challenges ahead.
Common symptoms during this stage
During the preclinic stage of Alzheimer’s, individuals may not display any noticeable symptoms.
Nonetheless, behind the scenes, changes are occurring within the brain.
This stage involves abnormal proteins accumulating in the brain, resulting in the formation of plaques and tangles.
Although symptoms may be subtle, diagnostic tests and evaluations can reveal these early brain changes.
Such tests can include brain imaging, genetic testing, and cognitive assessments.
Detecting Alzheimer’s during this phase can lead to early intervention and treatment, thus providing hope for managing the disease and possibly delaying the onset of more significant symptoms.
Diagnostic tests and evaluations
During the preclinic stage of Alzheimer’s, individuals may not display any noticeable symptoms.
Nevertheless, diagnostic tests are essential in identifying early signs of the disease.
Professionals employ various methods, including cognitive assessments, brain imaging techniques like PET scans, and genetic tests to test memory and thinking abilities, as well as the presence of any inherited genetic factors.
These diagnostic measurements provide valuable insights into the individual’s cognitive health, aiding in identifying potential future risks of acquiring Alzheimer’s.
Although the preclinical phase may not be characterized by noticeable symptoms, early detection through comprehensive clinical evaluations sets the foundation for effective intervention strategies and support for individuals and their loved ones.
Stage 2: Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI)
Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) is the second stage in the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
During this stage, individuals may exhibit more noticeable memory loss and difficulties with language, decision-making, and problem-solving.
Although still deemed mild, MCI represents a crucial early intervention and treatment stage.
The diagnosis comes from a comprehensive evaluation encompassing cognitive assessments and medical exams.
Various therapeutic interventions, such as medication and cognitive rehabilitation, can help prevent the progression of MCI.
It is crucial for individuals, along with their caregivers, to seek support and resources to navigate through the challenges and plan for the future.
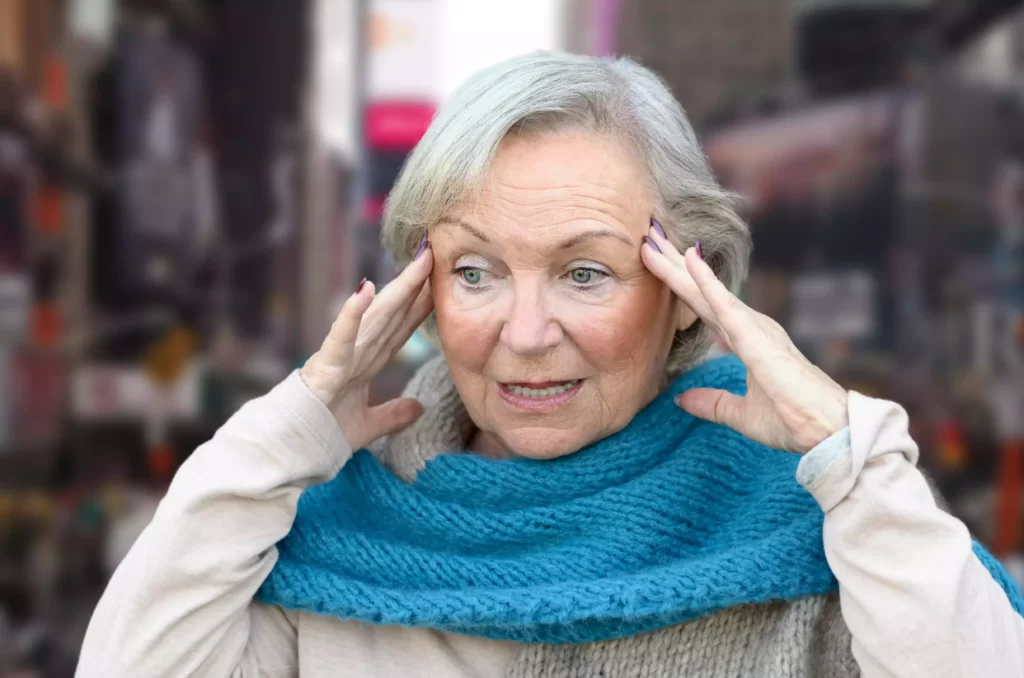

Early signs and symptoms of MCI
During the early phases of Alzheimer’s Disease, commonly known as mild cognitive impairment (MCI), individuals may notice subtle changes in their memory and mental abilities.
These changes may include forgetting recently held conversations or events, misplacing belongings, difficulty making decisions, and trouble planning and organizing.
Despite not affecting daily activities that much, these symptoms frequently concern individuals and their loved ones.
Observing these signs and seeking medical assistance for a proper diagnosis is essential.
Detecting MCI early can lead to timely interventions and treatment strategies that could halt the progression of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Progression from preclinical Alzheimer’s
The second phase of Alzheimer’s is categorized as mild cognitive impairment (MCI).
During this phase, individuals may have occasional memory lapses and difficulty forming the right words.
Although these symptoms don’t always signify Alzheimer’s disease, these symptoms can serve as early warning signs.
MCI is a phase between normal aging and the more severe cognitive decline caused by Alzheimer’s.
It is worth noting that not all individuals who are diagnosed with MCI will go on to develop Alzheimer’s disease.
Medical professionals can precisely diagnose MCI by combining assessments and tests.
Early detection enables the implementation of treatment options and interventions to halt the disease’s progression potential.
Diagnosis and treatment options
During Alzheimer’s stages, diagnosis and treatment are vital in regulating the disease.
Individuals may encounter mild memory loss and cognitive difficulties in the initial phase, referred to as mild cognitive impairment (MCI).
To diagnose MCI, healthcare professionals employ various assessments, including medical history, cognitive tests, and neuroimaging scans.
Once diagnosed, it’s crucial to investigate treatment options, including cognitive-enhancement medications, lifestyle interventions, and support from caregivers and Alzheimer’s organizations.
Early intervention may be able to slow down Alzheimer’s disease progression, enhance the quality of life, and provide essential support for both patients and their loved ones.
Stage 3: Mild Alzheimer’s
Stage 3 of Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by mild cognitive impairment and memory loss, significantly impacting daily life.
Individuals in this stage may need help remembering names, finding the right words, and frequently misplace items.
Complex tasks such as managing finances or planning events become increasingly challenging.
As a caregiver, it is essential to provide support and assistance while encouraging independence.
Creating a structured environment and implementing memory aids can help ease the difficulties faced by those with mild Alzheimer’s.
Understanding the unique needs of individuals in this stage is crucial for providing appropriate care and support.
Definition and characteristics
Stage 3 or Mild Alzheimer’s is known as “Mild Alzheimer’s.” During this phase, individuals typically display noticeable memory loss and cognitive decline yet can still function autonomously.
Common characteristics involve forgetfulness of recent events, difficulty with word retrieval, and challenges with organizational skills.
Even though these changes might be concerning, individuals with mild Alzheimer’s can still engage in daily activities and maintain relationships.
Caregiving and supporting strategies during the present stage primarily focus on promoting independence while assisting when necessary, creating a safe and exciting environment, and supporting the individual and their loved ones emotionally.
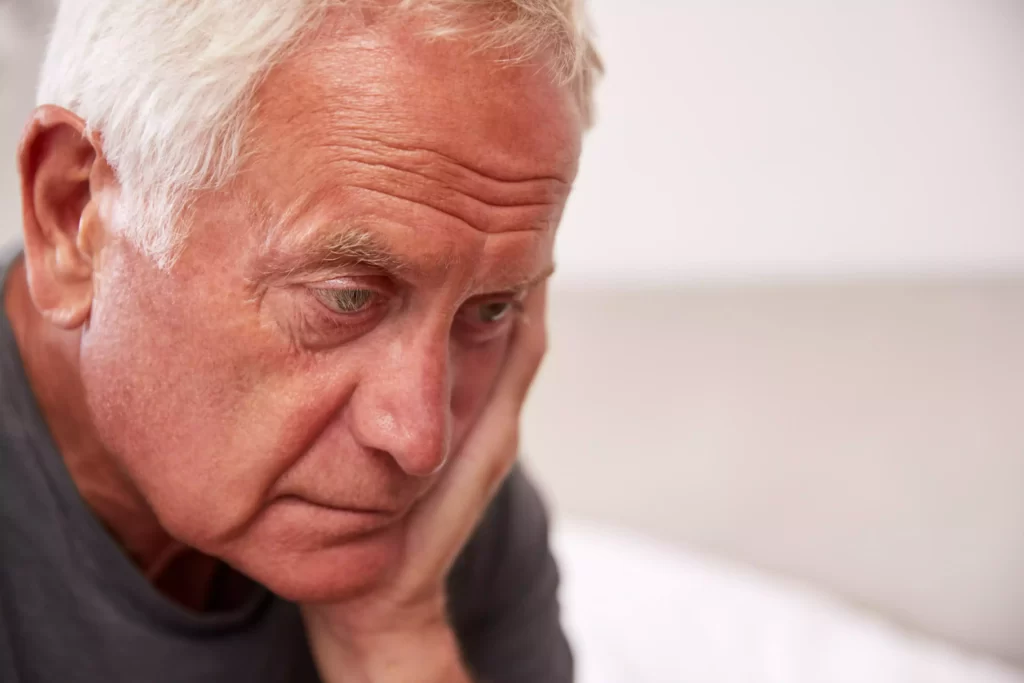

Challenges faced by individuals with mild Alzheimer’s
Individuals currently diagnosed with mild Alzheimer’s face unique challenges as their cognitive decline progresses slowly.
Memory loss may become more evident, affecting daily activities like recalling appointments or recent events.
Difficulties with focus and decision-making may arise, causing it to be harder to perform familiar tasks. Puzzlement and confusion can often surface during social interactions, causing withdrawal or frustration.
These challenges may cause anxiety and depression among those with mild Alzheimer’s.
And understanding from a professional is crucial to providing appropriate guidance, engaging in engaging activities, and creating a supportive environment that supports independence and quality of life.
Strategies for caregiving and support
Professional care and support are required when assisting individuals in the mild stage of Alzheimer’s.
First and most importantly, routines can immensely benefit from providing structure and familiarity.
It is crucial to promote independence as much as possible while ensuring that assistance is provided where required.
It can easily be achieved through simplifying tasks, breaking them down into manageable steps, and eliminating distractions.
Effective communication involves using clear and straightforward language while keeping eye contact, which can aid in understanding.
Moreover, fostering a safe and engaging environment can significantly enhance the individual’s well-being.
By employing these strategies, caregivers can provide the necessary support for those with Alzheimer’s.
Stage 4: Moderate Alzheimer’s
Moderate Alzheimer’s is the most common stage of Alzheimer’s disease, indicating a significant decline in cognitive abilities.
Individuals in this stage frequently experience memory, language, and problem-solving challenges.
They may require help with daily tasks and have difficulty engaging in social interactions.
This stage can be characterized by increasing confusion, inability to recall recent events, and difficulty managing personal hygiene.
Caregivers are vital in assisting and safeguarding those with moderate Alzheimer’s.
Effectively managing the symptoms requires employing coping mechanisms like developing routines and maintaining a calm atmosphere.
Furthermore, it is vital to consider possible future care options and seek guidance from experienced professionals to ensure that those suffering from Moderate Alzheimer’s enjoy the best quality of life.
Worsening symptoms and challenges
In the moderate Alzheimer’s stage, individuals notice an increase in the severity of their symptoms and must overcome new challenges daily.
Memory loss gradually becomes more oblique, causing difficulties recalling recent and essential details.
Tasks that used to be simple, such as organizing or planning, are now becoming more challenging.
Moreover, communication skills are deteriorating, with individuals experiencing difficulty choosing the right words or engaging in meaningful conversations.
This stage can also lead to behavioral changes, such as restlessness, agitation, or social withdrawal.
As relatives of those affected, it is crucial to be aware of these worsened symptoms and challenges to provide the necessary support and care.

Progression from mild Alzheimer’s
As Alzheimer’s progresses, individuals progress from the mild stage to moderate Alzheimer’s, where symptoms become more vigorous and challenges escalate.
During this stage, memory loss intensifies, causing individuals to have difficulty recalling recent events or recollecting personal details.
Additionally, these individuals may struggle to communicate clearly and coherently. Tasks such as managing finances, cooking, and driving have become more challenging.
Caregivers, family members, and friends must provide support and employ coping mechanisms to assist in daily living activities.
Additionally, professional assistance, such as local home care or memory care facilities, may ease some of the burdens and provide the necessary care during the disease’s progression phase.
Coping mechanisms and assistance available
In the phase of moderate Alzheimer’s, individuals experience a significant decline in cognitive abilities.
Memory loss has intensified, making recalling recent events or identifying family members and friends more difficult.
Nonetheless, coping mechanisms are available to assist in navigating these challenges. Professional caregivers and specialized memory facilities can provide support and supervision to ensure the safety and well-being of the individual.
These professionals have been specifically trained to utilize techniques and strategies specific to the needs of those with Alzheimer’s.
Therapy programs, including adaptive technologies, can assist in improving communication skills as well as promoting engagement and memory retention.
Seeking professional assistance and effectively leveraging available resources enhance the quality of life for those with Alzheimer’s and their loved ones.
Stage 5: Severe Alzheimer’s
Stage 5 consists of a severe decline in cognitive function, leaving individuals largely dependent on others for their daily activities.
Advanced symptoms and problems, such as significant memory loss, disorientation, and difficulty communicating, become increasingly common during this stage.
And well-being is paramount when a patient has Alzheimer’s disease. Alternative palliative care may also provide comfort, manage symptoms, and enhance the quality of life.
As professionals, it is crucial to comprehend the challenges faced by individuals with severe Alzheimer’s and provide compassionate and comprehensive care while also accompanying their families and caregivers throughout this challenging journey.
Advanced symptoms and complications
During the advanced stages of Alzheimer’s, individuals experience a significant decline in their cognitive abilities.
Memory loss may worsen, and memory may be impaired, causing memory to become challenging to identify.
Memory loss often results in language skills needing to be recovered, making communication incredibly tough.
Individuals may display behaviors that are difficult to manage, such as agitation, aggression, or wandering.
Basic self-care activities have become challenging to perform autonomously, and there is a high risk of falls and injuries.
Caregivers and family members must determine full-time care options for individuals with severe Alzheimer’s, whether in nursing homes or specialized facilities.
Palliative care, which focuses on providing support and improving the quality of life, has become essential to their care.
Full-time care and nursing considerations
During the advanced phase of Alzheimer’s, also called stage 5 or 3, individuals may experience severe symptoms and complications.
As dementia progresses, full-time care becomes increasingly essential for the well-being and safety of the person with Alzheimer’s.
This stage commonly requires specialized nurses to treat individuals’ challenges, such as difficulty with mobility, feeding, and speech.
Caregivers and health professionals ensure that those with severe Alzheimer’s are well-cared for and protected.
Additional palliative care may help alleviate pain and discomfort and ensure the highest quality of life possible during this stage of the disease.
Palliative care options for individuals with severe Alzheimer’s
Palliative care is vital in ensuring the recovery of individuals with severe Alzheimer’s disease.
As Alzheimer’s progresses into the advanced stages, patients tend to notice a significant decline in cognitive function and overall health.
During this challenging phase, specialized full-time care and nursing considerations become essential to ensure the comfort and well-being of the individual.
Palliative care provides a holistic approach, focusing on symptom management, pain relief, and emotional support.
This specialized therapy aims to enhance the quality of life for patients and their families.
Palliative care specialists tirelessly strive to accommodate the unique needs and challenges of individuals diagnosed with severe Alzheimer’s, providing compassionate and individualized care that aims to improve their overall well-being.

Conclusion
In conclusion, recognizing the stages of Alzheimer’s disease is crucial in providing comprehensive care and support for individuals and their families.
Early detection enables timely intervention and treatment options.
By understanding the progression of Alzheimer’s from preclinical Alzheimer’s to mild cognitive impairment and, ultimately, severe Alzheimer’s, caregivers can better anticipate and adapt their caregiving strategies accordingly.
It is important to properly utilize available resources and support networks to manage Alzheimer’s disease successfully.
Current research in this field offers hope for advancements in diagnosis, treatment, and potential prevention methods. Together, let’s be the voice for those who have Alzheimer’s.
Importance of early detection and understanding the stages
Identifying and understanding the stages of Alzheimer’s disease is crucial to providing optimal care and support for individuals and their families.
Recognizing the early symptoms of memory loss enables medical professionals to promptly initiate appropriate interventions and treatment plans.
Additionally, comprehending the stages helps caregivers prepare and anticipate the diverse challenges that arise during each phase of cognitive decline.
By actively studying and seeking guidance, individuals can make informed decisions about care options, efficiently utilize available resources, and provide the best possible support for their loved ones during their Alzheimer’s journey.
Available resources and support for individuals and caregivers dealing with Alzheimer’s
Individuals and caregivers should not feel isolated or overburdened when dealing with Alzheimer’s disease.
Numerous resources, including support systems, are available to aid them throughout the various stages of Alzheimer’s disease.
Organizations such as the Alzheimer’s Association provide a wealth of information, support groups, and educational programs to assist individuals with Alzheimer’s.
Additionally, specialized care services, home healthcare services, and respite care options can ease caregivers’ burden.
Understanding the available support and seeking qualified professionals improve the well-being and quality of life for those diagnosed with Alzheimer’s and their caregivers.
Future prospects and ongoing research in Alzheimer’s disease
The prospects and ongoing studies in Alzheimer’s disease hold promise in developing treatments and finding a cure for this debilitating condition.
Research doctors are unfailingly tinkering with Alzheimer’s, diligently pursuing potential biomarkers, genetic factors, and novel therapeutic approaches.
Advancements in technology, such as neuroimaging and genetic testing, allow earlier diagnosis and intervention, which can have a better life for patients and their families.
Collaboration among scientists, clinicians, and caregivers is crucial for understanding Alzheimer’s and devising innovative strategies to combat its progression.
Despite the challenges, the persistent pursuit of knowledge offers hope that this debilitating disease can be overcome someday.














0 Comments